Treatment Guide
Alcohol use disorder (AUD) is the clinical term for alcohol addiction or alcoholism. It is a chronic, relapsing medical condition that requires long-term care. People with AUD exhibit compulsive behavior around alcohol use — for example, drinking more or more often than intended, craving alcohol when not drinking, and continuing to drink despite negative consequences. AUD can be mild, moderate, or severe depending on how many symptoms a person has. Learn more about diagnostic criteria for AUD>
Alcohol use disorder is treatable; many people recover from AUD and go on to live healthy, productive lives. Learn more about long term recovery>
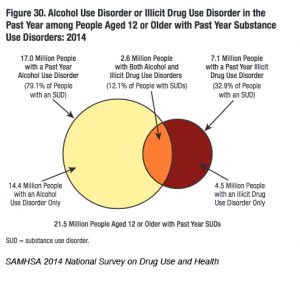
The public health costs related to AUD are staggering. An estimated 88,000 Americans die every year due to alcohol-related causes, making it the fourth leading cause of preventable death in the U.S. Nearly 70% of substance use disorders are attributed to alcohol only, with another 12% attributed to alcohol and another drug combined [1]. This amounts to 17 million people addicted to alcohol in the U.S., yet fewer than 10% of those people receive treatment.
AUD is associated with poor health outcomes including alcoholic liver disease, brain damage, heart and circulatory disease, and others. Learn more about health consequences of AUD>
How is AUD treated?
AUD has multiple facets: physical, emotional, behavioral, social, and spiritual. A sound treatment plan uses a diverse set of strategies to address these elements according to an individual’s needs. Relapse is common on the road to recovery and is typically a sign that treatment needs to be adjusted. Currently, there is no silver bullet or one-size-fits all treatment for AUD — each person can and should individualize their treatment plan to fit their needs and circumstances. Some people need medically-supervised detoxification in a clinical setting; others can begin by contacting an addiction psychiatrist who can prescribe medication and set up counseling. Still others may wish to begin by attending a mutual help group meeting to learn about others’ experiences. There are many pathways to recovery. Learn more about the available options by exploring our treatment guide>
National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) Principles of Effective Treatment>
National Institute on Alcoholism and Alcohol Abuse (NIAAA) Alcohol Facts and Stats>
American Society of Addiction Medicine Definition of Addiction>
NIDA: Understanding Drug Use and Addiction>
Related: Scientific review by experts explains disease model of substance use disorder>
SAMHSA 2014 National Survey on Drug Use and Health>